Next-Gen Telematics: Revolutionizing Utility Fleet Management with AI and Data Analytics
Xylem Kendall manages a fleet of more than 5,500 rolling assets, ensuring efficiency and reliability across every aspect of vegetation management operations. The company’s effective fleet management strategy is more than making schedules and managing logistics — it’s about measuring performance, streamlining operations and staying ahead of customer demands across the entire fleet lifecycle. Today, fleet management is entering a new era, driven by advancements in automation, artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics.
By leveraging telematics, fleet managers can boost efficiency, reduce expenses and proactively address maintenance and safety concerns before they become timely and costly problems. Companies that adopt these emerging technologies can better track and measure performance metrics, enhance on-the-road safety and make informed, data-driven decisions.
Understanding both the benefits and challenges of implementing these technologies into the fleet management lifecycle is essential for organizations looking to maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly tech-forward industry.
History of Telematics
Telematics, the integration of telecommunications and informatics, traces its origins to the 1960s when the Department of Defense developed the Global Positioning System (GPS), which was initially designed for military and aviation use. In the 1980s, advancements in computer technology and telecommunications enabled GPS to integrate with various data systems, laying the foundation for telematics. By the mid-1990s, the internet gained traction, and GPS became widely available to civilians, further advancing telematics and enhancing its sophistication.
In recent decades, telematics technology has expanded exponentially, driven by improvements in GPS, cellular networks, AI and data analytics. Today, telematics systems are indispensable tools for fleet managers, providing real-time data and insights on vehicle location, driver behavior, usage patterns and maintenance needs. These capabilities will continue to evolve, particularly in the automotive segment.
According to Mordor Intelligence, the Smart Fleet Management Market is projected to reach $737.09 billion by 2029, growing at a 9.5% Compound Annual Growth Rate from 2024 to 2029. As the industry scales, we are entering a new era: Next-Gen Telematics.
What is Next-Gen Telematics?
The future of telematics is marked by the application of powerful AI capabilities and machine learning, advanced data analytics and remote diagnostics to monitor, manage and optimize fleet operations.
Next-Gen telematics revolves around the ability to process and learn from vast amounts of data in real time. Modern telematics systems are equipped with sophisticated analytics capabilities that provide organizations valuable insights and comprehensive reporting. By harnessing AI and machine learning, these systems go beyond simple tracking — they actively recognize and analyze patterns, forecast outcomes and deliver actionable insights that enhance fleet performance. By converting raw data into meaningful reports, businesses can pinpoint areas for improvement and implement strategic changes that yield measurable results.
This advanced capability translates into several key benefits for fleet management:
- Predictive Maintenance: These technologies enable fleet managers to proactively track asset conditions, assess performance and anticipate maintenance needs before issues escalate, reducing breakdowns, downtime and repair costs. By leveraging telematics-enabled remote diagnostics, managers can monitor key data points such as battery condition, brake performance, engine temperature, emissions, lubricant levels, pressure and vibrations. Instant alerts notify them of potential mechanical issues, allowing for timely intervention before minor concerns turn into costly repairs. This proactive approach streamlines maintenance efforts and extends vehicle lifespan.
- Driver Behavior Analysis: AI systems can detect risky driving behaviors such as speeding, rapid acceleration and hard braking. Dashcams play a crucial role in identifying distracted driving and providing real-time, tailored feedback to help improve driver behavior.
- Operational Optimization: Using both historical and real-time data, fleet managers can optimize daily routes, fuel consumption and vehicle usage. These intelligent systems continuously analyze traffic patterns, weather conditions and driver behavior, enabling dynamic route adjustments and efficient resource allocation. Over time, they learn and adapt to changing conditions. As an example, Xylem Kendall leverages daily vehicle utilization information, including run and idle times as well as distance traveled, to enhance productivity, lower cost and improve overall fleet performance.
Telematics in Action
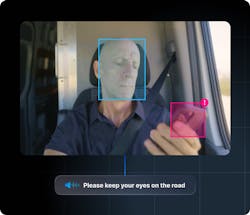
Safety remains a top priority in fleet management, and next-gen telematics solutions are transforming risk mitigation. AI-powered dash cameras monitor driver behavior in real time, detecting distractions, drowsiness and other unsafe actions, while collision avoidance systems — such as lane departure warnings and automated alerts — provide critical feedback to help prevent accidents and enhance road safety.
Driver-facing cameras are instrumental in detecting distractions, such as cell phone use or safety issues, like not wearing a seat belt. The technology sends real-time alerts to drivers, fostering immediate behavior change. Leaders should also follow up with post-trip coaching sessions regarding the detected safety risk. Driver notifications and training will help improve driver behavior and reduce the risk of accidents caused by inattentiveness. This is backed by a transportation study that found AI-powered dashcams significantly reduced accidents by 22% and unsafe driving incidents by 56%.
To illustrate the impact of these innovations, let’s examine a practical implementation involving AI cameras.
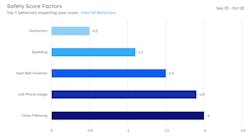
One of the most critical metrics in fleet management is the driver safety score, which evaluates driving behavior based on events like harsh braking, speeding and distraction. Each driver has an individual score, and these can be aggregated into a team power score, giving general forepersons and supervisors a comprehensive view of the fleet’s overall performance.
By monitoring these scores, companies can identify trends that impact safety. For example, when Xylem Kendall introduced in-cab cameras, data revealed that cell phone use was a leading factor in lowering scores. In response, the company installed hands-free phone holders in every vehicle. This small but strategic change resulted in a 5% improvement in overall driver scores — demonstrating how telematics-driven insights can lead to measurable improvements in safety and compliance.
Road-facing cameras also play a crucial role, capturing external events such as speeding, traffic sign violations, collisions or near misses. Using AI, organizations can analyze this footage to determine root causes, allowing them to better understand driver behavior and develop targeted trainings to improve safety.
Challenges and Considerations
As fleet management embraces cutting-edge technology, organizations must also address key challenges that come with implementation. From privacy concerns to compliance and training, understanding these hurdles is crucial for a smooth transition and long-term success.
Privacy Concerns. One of the most significant challenges is balancing continuous monitoring with driver privacy. Employees may feel uneasy about being constantly tracked, which can impact morale. Addressing these concerns through transparent communication and clear policies is critical to gaining driver buy-in and building trust.
Upfront Costs. Implementing advanced fleet technologies requires a substantial initial investment in hardware, software and integration. However, long-term savings from reduced accidents, improved fuel efficiency and more efficient operations outweigh these costs.
Training and Adoption. To fully leverage these technologies, fleet managers and drivers must be properly trained. Without adequate education and hands-on experience, tools may go underutilized, limiting their potential benefits. Investing in comprehensive, user-friendly training programs ensures smoother adoption and maximized ROI.
Legal and Compliance. Data privacy laws, particularly those governing video surveillance and location tracking, must be strictly followed. Organizations must ensure compliance to protect both their drivers and their business.
Practical Tips to Implement Dashcam Monitoring
To successfully integrate AI-powered dashcams, organizations must focus on transparency. Clearly communicating the purpose of the cameras, emphasizing safety improvements rather than surveillance, helps alleviate driver concerns. Establishing clear policies on video usage and access to cameras further builds trust among drivers and ensures consistency in implementation.
Encouraging engagement through creative strategies like gamification can improve adoption rates. Rewarding top-performing drivers and challenging regions to achieve the best safety scores each month fosters a positive approach to technology adoption. Also, don’t forget to celebrate the wins. Be sure to highlight not-at-fault events and close calls — this helps showcase the effectiveness of AI cameras and reinforce their value to the organization.
Managing costs is another key consideration. Organizations should explore financing options or phased deployments to manage the financial impact. A strategic rollout allows companies to spread out initial costs while focusing on long-term return on investment from accident reduction and operational improvements.
Future Trends
AI-driven innovations are shaping the future of fleet management. Advanced AI will analyze vast amounts of data to predict maintenance needs, prevent accidents and optimize routes in real time. Predictive analytics will play a vital role in reducing vehicle downtime and improving overall fleet efficiency.
Telematics will also become increasingly integrated with autonomous vehicles. As self-driving technology progresses, telematics will be essential for managing both semi-autonomous and fully autonomous fleets, improving safety, optimizing logistics and ensuring regulatory compliance.
AI-powered cameras will continue to evolve with more advanced driver assistance systems. Features such as automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assistance and real-time driver health monitoring will further reduce accidents and improve overall road safety.
Augmented reality (AR) dashcams may soon become a reality. These next-generation cameras may incorporate AR technology to provide real-time navigation overlays, hazard alerts and immersive driver training, offering a new level of situational awareness for drivers.
In this new era of fleet management, cutting-edge technologies like telematics and AI are transforming operations, offering fleet managers unprecedented opportunities to boost efficiency and safety. Beyond operational improvements, these advancements also drive significant cost savings. By implementing predictive maintenance and minimizing accidents, fleet managers can prevent breakdowns, reduce repair expenses and extend the lifespan of fleet assets.
Companies that embrace these emerging technologies will not only enhance their fleet performance but also position themselves as industry leaders, thriving in a highly competitive market.