Utilities are making major changes as they strive to decarbonize, decentralize and digitalize their power grids. Grid applications will play a central role in helping them succeed with these changes while ensuring that the power system remains safe and resilient. For many utilities, the main step in this transformation will be to bring new automation capabilities to transmission and distribution substations.
Conventional substations today have transformers and switches in the switchyard that connect and disconnect power lines and cables at different voltage levels. Copper lines typically carry analog output from this equipment to the substation control house, where controller units and relays acquire the line data and perform critical protection, monitoring and control functions.
Early electromechanical relays and controllers had limited communication capabilities. This made it expensive for utilities to install, operate, maintain, reconfigure and troubleshoot substations. In the 1980s, the introduction of microprocessors turned relays and controllers into intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) that could perform protection, control, local and remote monitoring in real time. This was the dawn of substation automation.
The strong communication capabilities of IEDs meant that a utility could use a few fiber optic cables to replace hundreds or thousands of meters of copper wires that ran between the switchyard and the IEDs in the substation control house. By installing fiber cable, utilities could prepare for the era of digital substations.
The industry recognized that open, standards-based communication would be the key to unlocking the many potential operational and business benefits of IEDs. In 2003, IEC Technical Committee 57 published IEC 61850, “Communication networks and systems in substations,” a suite of standards that provides a communication foundation for digital substations. This suite uses standard communication protocols to provide a framework that ensures interoperability among protection and control devices from different vendors. It also provides a powerful substation configuration language that facilitates system design and engineering and device configuration.
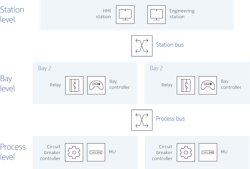
IEC 61850 defines a three-level digital substation architecture with two substation buses, which are Ethernet LANs. The architecture’s bottom level is made up of equipment such as merging units and circuit breaker controllers, which act as the digital interface for primary switchyard equipment. The process bus connects this bottom level to the architecture’s middle level, which includes secondary IEDs such as the bay controllers and relays in the substation control house. The middle-level IEDs also connect with each other and the station equipment in the architecture’s top level using the station bus, another Ethernet LAN.
Fig. IEC 61850-based substation network blueprint
Responding to the need for automation beyond the substation, TC 57 extended the IEC 61850 suite in 2010. Titled “Communication networks and systems for power utilities,” Edition 2 of the standard provides specifications for areas such as:
· Wide area network (WAN) communications between substations
· WAN communications between substations and control centers
· Field area network (FAN) communications between substation and distribution feeders
· Time synchronization
These new specifications enable utilities to support automation throughout the grid. However, it can be challenging for utilities to develop network blueprints that will enable them to take advantage of IEC 61850 everywhere. For example, utilities may need to consider the network service requirements of multiple communications domains (WAN, substation LAN and FAN) for use cases that depend on seamless, end-to-end connectivity. And grid assets such as merging units and phase measurement units require time synchronization with accuracy around 1 microsecond.
Utilities have started to express interest in extending virtualized cloud computing to substations to make their grids more efficient and agile. IEC 61850 can evolve to support virtualization use cases with seamless workload-to-workload interconnection that extends across the WAN to the utility data center.
Find out more
Download our white paper to learn more about how the IEC 61850 standard suite enables grid automation everywhere and the commercial, operational and environmental benefits it can bring to utilities.
Sponsored By: